

Get 93% OFF on Lifetime
Exclusive Deal
Don’t miss out this deal, it comes with Password Manager FREE of cost.
Get 93% off on FastestVPN and avail PassHulk Password Manager FREE
Get This Deal Now!By Nick Anderson No Comments 6 minutes
As a resource of information, the internet is unmatched. It is one of the biggest inventions in the world that has had the biggest impact on our lives than perhaps any other thing. The internet had witnessed several transformations over the years since its inception in the late 80s – when it used to be known as ARPANET. The latest evolution of the internet is being colloquially termed as “Web 3.0”. We’ve taken the opportunity to explain to you what is Web 3.0 and how it will shape the next generation of this digital space.

Before we explain what Web 3.0 is, you need to understand how the internet as we know it today came to be the interactive digital world that powers the billions of smart devices in the world.
In the early days of the internet – between the 90s and early 2000s – the internet had just become public, and computers were becoming affordable and began appearing in homes worldwide. It was also the time when graphical user interfaces were becoming common. The internet was a digital space that hosted static web pages. Web pages were far different than what we use today.
Think of static web pages that you can only read but cannot interact with beyond clicking on buttons. For example, here’s what eBay looked like in its early days.
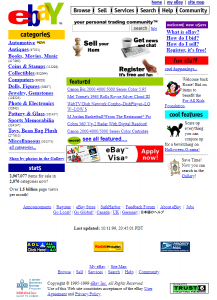
Notice how besides the lack of rich media, the web page does not show a personalized homepage according to the user’s interest. Regardless of who opens the web page, the web page’s contents will remain the same. Technologies didn’t exist back then that could harness the computing capabilities of the device and user data to deliver an experience that’s graphically exciting and relevant to the user. Even simple things such as comment boxes were implemented later.
But as web technologies got better, we entered a new age of the internet, known as Web 2.0. Thanks to technologies like CSS, HTML, Javascript, the new age involved interactive web pages with videos, ads, photo galleries, infinite-scroll pages, and more. But above all that, web pages could be tailored to put relevant information in front of the user based on interest.
It’s the reason why Google’s search results are not the same for everyone. It uses factors such as your browsing history and location to give you results more relevant to you. Cross-site tracking allows platforms such as Facebook to track your interest even when you’re not on social media.
The web became much more interactive. It is now possible to share an article from The New York Times on your social media account, live stream activity to followers, build an eCommerce store and target the right audience, upload videos, build marketplaces to sell and buy things, and create forums where users can express themselves through emojis. The internet now has a culture.
The idea behind the next phase of the internet is decentralization, which means that information will be hosted on a network of users, and user data will belong to the user.
Today, the web is very centralized. It is mostly big tech companies such as Google and Facebook controlling the internet. They own some of the top internet platforms in terms of the number of users and popularity. Meta (formerly known as Facebook) owns Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Oculus. And Google owns the biggest search engine and has other platforms that form an ecosystem of Google services.
The amount of data the big tech firms have on users is significant. The transition to Web 3.0 will mean the big tech companies will not control user data as the principles of a decentralized network mean that all users on the network are equal.
The new phase will be backed by blockchain technology that currently powers cryptocurrencies, and many other companies have also adopted it.
Blockchain is immutable, which means that information can only be added and not amended. It provides transparency and reliability to records because no one on the network can alter them. It’s what gives the end products like cryptocurrency a unique standing. There is no risk of fraud because everyone on the blockchain shares a general ledger that includes information about every transaction.
Web 3.0 will also be powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) to provide information based on context. In short, the core technologies that will pave the way for the new generation of the internet are blockchain and AI. Web 3.0 is also called the “Semantic Web” because AI will be able to deliver content based on context and not its literal meaning.
That is what the evangelists hope. As privacy advocates, we can stand behind technologies that improve user privacy. But decentralization of everything is not without downsides.
Decentralization is at the core of what Web 3.0 evangelists think when they envision the next phase of the internet. In many ways, it’s already here. The start of the cryptocurrency boom was the tipping point that accelerated the idea of decentralization and pushed businesses to adopt blockchain technology.
The latest trend and product of blockchain is NFT (Non-Fungible Token). NFT is a digital item that you can own exclusively. It is non-fungible because its ownership cannot be replicated. Imagine the Mona Lisa, but it was made as an NFT originally. Unlike its physical version, the digital version can only belong to you as the sole owner.
Nike recently acquired an NFT company for its vision of selling digital items to customers. As a customer, you can buy a limited edition pair of sneakers that no one else in the world owns.
The first disadvantage of Web 3.0 is that it’s easier said than done. The web today is centralized on a massive scale. Information is stored and processed by servers hosted by big tech companies that can allow or block access. Taking away this kind of control from companies who profit from user data and targeted advertisements will be very challenging, if not impossible.
Another downside is that you cannot censor the web. It’s a double-edged sword, but it can control hate speech, online sexual harassment, and cyberbullying when censorship is followed right.
The third disadvantage has to do with decentralization. Devices that are a couple of generations older will not have sufficient computing power to be a node in the network.
Much like metaverse, it’s hard to predict how Web 3.0 will ultimately look like or if the vision of decentralization evangelists will become a reality. But one thing is for sure, Web 3.0 is already here in the form of cryptocurrency and there has never been an easier way to make transactions that is also secure and free of fraud.
© Copyright 2025 Fastest VPN - All Rights Reserved.


Don’t miss out this deal, it comes with Password Manager FREE of cost.
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.