

Get 93% OFF on Lifetime
Exclusive Deal
Don’t miss out this deal, it comes with Password Manager FREE of cost.
Get 93% off on FastestVPN and avail PassHulk Password Manager FREE
Get This Deal Now!By Nancy William No Comments 61 minutes
In Windows, beyond the familiar graphical interface, lies the Command Prompt. This tool offers access to a vast list of command prompts, over 280 to be exact, allowing you to control the operating system directly through text instructions instead of relying on the mouse and icons.
TIP – Even though using command prompts is fairly safe for your device, there are external threats to look into. If you’re connected to free WiFi or even using third-party apps on your PC, ensure your connection is encrypted with the best VPN for it. FastestVPN offers an app for Windows and other devices to ensure full online protection.
Beyond basic tasks like copying files or formatting drives, the Command Prompt unlocks a hidden potential. From backing up your data to sending messages across computers, even restarting your own device, it offers a powerful range of control.
Additionally, savvy users can unlock further capabilities through clever combinations of these commands, offering a deeper level of interaction with your system.
That said, take a look below at the complete list of command prompts to use on Windows devices arranged in alphabetical order.
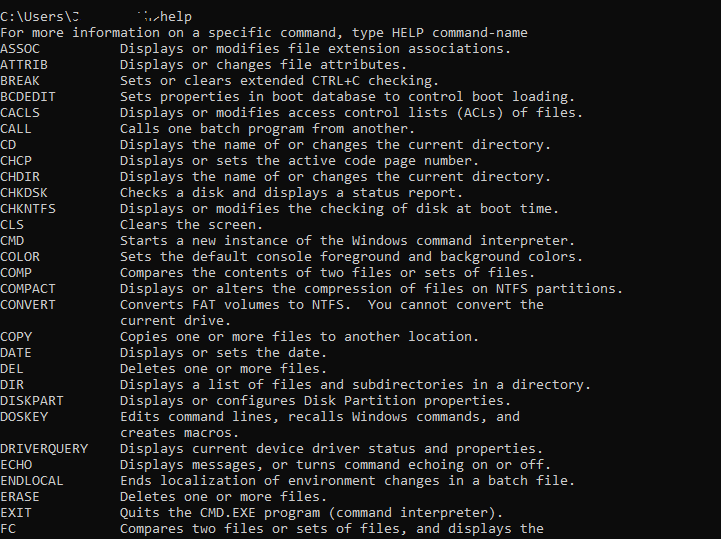
Our list of all the Command Prompt commands, or CMD commands below, is operatable on Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
All the commands for Windows 11-7 are known as Command Prompt commands, while the ones for Windows 98/95 or the MS-DOS. For them to work, you must launch the command line interface by type cmd in the search bar.
Here is a list of 7:
The At command is mostly utilized to arrange commands and other program schedules to operate at a particular time and date. This CMD prompt is accessible for Windows 7, Windows XP, and Windows Vista. For Windows 8, the command line scheduled tasks are completed with the schtasks command.
The append command, once used by programs to access files in different directories, is no longer supported in 64-bit versions of Windows. While still present in MS-DOS and 32-bit Windows versions, it’s recommended to find alternative methods for file access in modern systems.
Next on our list of command prompts is Assoc. The Assoc command lets you control file associations. You can use it to see or change which program opens different file types (identified by their extensions). This feature is available in all major Windows versions, from XP to Windows 11.
The ARP command is a useful tool used to display and manage the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache on your computer. Plus, since it’s available for all Windows versions, it is what makes it desirable.
The Atmadm command, once used to manage ATM connections, is no longer relevant in modern Windows systems. Support for ATM networks was discontinued, starting with Windows Vista, rendering Atmadm obsolete.
If there are any audit policies, the Auditpol prompt command is utilized to create changes or display them. For availability, this Command Prompt is operative for Windows Vista, Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.
The last of the (A) selections on our list of command prompts is Attrib. The Attrib command is available across various operating systems like DOS, Windows, and ReactOS. This command empowers users to control specific properties, known as attributes, of files and folders. With Attrib, you can modify aspects like read-only, hidden, or archive status, providing more control over your data organization.
They are:
Behind the scenes of your Windows boot process lies a hidden store called Boot Configuration Data (BCD). Think of it as a recipe book, dictating which applications (like your operating system) and settings are used during startup. To manage this recipe book, you have the BCDEdit command line tool. It aids in creating new boot entries, customizes the boot behavior, and helps modify all existing entries.
The Bootcfg CMD prompt has reached a legacy status in terms of Windows boot configuration management. Even if still available in Windows 10, 8, 7, and Vista, it no longer serves a practical purpose. Modern Windows versions have replaced the boot.ini file, which bootcfg interacts with, with a newer and more robust approach utilizing the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) store. The recommended and supported approach for managing boot configurations in these systems is to leverage the BCDedit command. This ensures compatibility and alignment with best practices for contemporary Windows environments.
The Bdehdfg command prompt offers disk partition characteristics of the specified drive. When you operate the Bdehdcfg command, it offers primary and logical information on the drive partition characteristics and the total size of the drive, displays or identifies the drive letter like (C: or D:), and gives you an estimation of the maximum free storage available. This command is available for Windows 11, 10, 8, and 7.
While you might find the Break command lingering in your system, it’s no longer relevant for its original purpose. This command, present in both MS-DOS and older Windows versions, controlled how the system responded to pressing Ctrl+C. However, in modern Windows (XP and beyond), it doesn’t have any effect on its own. This is because newer Windows versions handle Ctrl+C differently and don’t require the break command for functionality.
While the bitsadmin command is still technically present in Windows (11, 10, 8, 7) and Windows Vista, it’s gradually being retired. Microsoft recommends switching to the BITS PowerShell cmdlets for managing download and upload jobs instead. These cmdlets offer a more modern and efficient approach to accomplishing similar tasks. Consider migrating to PowerShell cmdlets for future-proofing your workflows.
BCDBoot, a command-line tool, empowers you to manage boot files for your Windows system. It is used for a Fresh Windows installation. For instance, after applying a new Windows image, you can use BCDBoot to configure the boot files and ensure your system starts up correctly.
Bootsect.exe is a handy tool for Windows users that deals with the inner workings of your system’s boot process. It helps to switch Bootloaders, which means if there is a need to change between Bootmgr and NTLDR (older Windows bootloaders), the Bootsect.exe can handle that for you. It also aids in Boot Sector Repair. For instance, if your computer’s boot sector (a crucial part for starting up) gets corrupted, Bootsect.exe can help restore it, potentially getting your system back on track.
They are:
In Windows, controlling who can access your files and folders is crucial. Two command-line tools, Cacls and its updated version iCacls, help you manage these access permissions. These tools work by interacting with security descriptors, which act like blueprints defining who can access a specific file or folder and what actions they can perform (read, write, modify, etc.) While cacls was the original tool, it’s recommended to use the newer and more powerful icacls for managing file access. Both tools are available on Windows and ReactOS.
If you’re looking for a way to locate your PC’s files and folders, the Chdir command prompt is the best. This versatile tool, available in all Windows versions and even MS-DOS, has two main functions: Showing your location and Changing your location. It lets you see the current drive letter and directories that you’re working in. Also, if you want to switch to a different folder or drive, use Chdir followed by the new path, and it navigates you there immediately.
As tasks handled by the Chdir command prompt mentioned above, the Cd command prompt is the shorthand version of it. It offers the same functionality with a briefer syntax. So, whether you prefer the classic CHDIR or the shorter Cd, both commands will help you move around your file system with ease.
The call command in Windows and MS-DOS is your secret weapon for nesting scripts within scripts. It allows you to execute one script from another, effectively creating a hierarchy of commands. This can help break down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. However, Call Command only works its magic within batch files, so running it directly at the Command Prompt or MS-DOS prompt won’t do much.
Next on the list of command prompts, we have Certutil. Windows (11, 10, 8, 7, Vista) offers the Certutil command for managing digital certificates and CAs (Certification Authorities). It primarily functions to view CA information but also has other CA-related features geared toward more technical users.
The Certreq command is a powerful tool available in Windows that allows you to manage digital certificates used for secure communication and authentication. Its key function is to request certificates for a new certificate from a Certification Authority (CA). You can also use it to retrieve certificates and manage the existing ones. Other advanced features include functionalities like enrolling for certificates using smart cards, exporting certificates to different formats, and installing certificates on remote computers. It’s available for Windows 7 and later versions, including Windows 11, 10, 8, and Vista.
The Chgusr command prompt helps to change or manage the install mode for the “Remote Desktop Session Host server” and is operatable on Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. However, note that this command prompt was replaced with the Change command.
The Change command prompt acts as a control panel for various settings. With Change, you can adjust installation modes and configure how applications are installed and deployed on the server. It also connects devices that rely on these communication ports to the server and controls how users log in to the server, including session timeouts and security options. This functionality is available in Windows versions from 11 and all the way to Vista.
In Windows (11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP), the cipher command acts as a guard for your data. It allows you to view the encryption status by checking whether your files and folders on NTFS partitions (a specific file system type) are encrypted, offering an extra layer of security. It further encrypts or decrypts specific files and folders, giving you control over which data you want to safeguard with additional protection.
The Chkntfs shows the file system type of your chosen disk drive. It runs automatic check-ups. If scheduled, it reveals if the drive needs checking at the next startup or is already clean. You can operate this command prompt in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, and XP.
The Chkdsk command prompt has three major purposes: it scans and fixes, maintains the health of your system, and looks over the entire computer’s hygiene. The CHKDSK is a built-in Windows tool that scans your hard drive for errors, acting like a doctor for your disk. It fixes all errors, helping your system data to be organized and running smoothly. Regularly running CHKDSK is like good computer hygiene, promoting optimal system health.
Next, we have the Comp command prompt. This CMD utility compares two file contents or even multiple sets of files. This comp command is operable for Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
In Windows, the Cscript command acts as a script interpreter, allowing you to run scripts written in various languages like VBScript. This makes it a powerful tool for automating tasks, including printer management. A popular use case is managing printers using scripts like prncnfg.vbs and others for configuration, drivers, and management. The other perk is that it automates repetitive tasks. This means that you can write scripts to automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency. This functionality is available in all versions of Windows.
CheckNetIsolation empowers Windows users to manage how their Windows Store apps connect to the network. You can see which apps can access the internet and gain transparency into which apps have permission to connect to online servers. This command also prompts restricting app access for security or privacy reasons. It allows you to limit specific apps from accessing the network entirely. This tool is available in all Windows environments, giving you more control over your app’s network behavior.
On Windows (11 – Vista), the Chglogon command grants you control over user logins on Terminal Servers. With it, you can enable logins, which allow users to connect to the server, and disable logins, which temporarily block new user connections. Other than that, the Chglogon command prompt drains logins. This allows current users to finish but prevents new logins. However, note that chglogon works the same as the change logon command!
In simple terms, the chcp command prompt acts like a translator for your computer. It lets you see or change the language encoding used to display characters on your screen. This is important because different languages use different sets of symbols, and chcp ensures things appear correctly. It’s available in all Windows versions and even in MS-DOS.
While the chgport command may have been a relevant tool in the past for managing COM port mappings in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, and Vista, it’s recommended to utilize the more current and supported change port command. This ensures compatibility and alignment with best practices for contemporary Windows environments.
The choice command prompt lets scripts offer users options and capture their selections. However, it’s missing in Windows XP. Instead, use the set command with the /p switch for XP compatibility. This provides an alternative way to achieve similar functionality in your scripts.
The cmd command, in simpler terms, opens the door in Windows (11 – XP) that opens a new command prompt window. This window allows you to interact with your computer using text-based commands instead of the usual mouse and clicks.
The Clip command prompt allows you to copy and paste across apps. Simply copy text from the command prompt and paste it into any program that accepts text. This clip command operates on Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
The Cls command offers a convenient way to improve the visual clarity of your Command Prompt environment. By executing cls, you can effectively remove all displayed commands and text, providing a clean slate for your next actions. It is accessible for MS-DOS and all Windows versions.
The cmstp command in Windows allows you to manage Connection Manager service profiles. These profiles store settings for how your device connects to networks, including internet connections, and are available for Windows (11,10, 8, 7) and Windows (Vista and XP.)
With the cmdkey command prompt, you can create, move, or show all stored passcodes and user names on your device. It is operable on Windows Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista.
The copy command in Windows and MS-DOS serves as a straightforward way to duplicate files. Simply tell it which file(s) you want to copy and where you want them placed, etc. However, if you need more advanced features like copying entire directory structures or preserving file attributes, consider using the more robust xcopy command. Think of copy as the basic file copier, while xcopy offers additional options for more complex needs.
The color command lets you change the colors of your command prompt window. You can choose different combinations for the text (foreground) and background to personalize your experience.
The command command prompt is a veteran of the MS-DOS era. It is used to launch the command prompt environment and is accessible for all 32-bit Windows versions. However, it’s no longer available in modern 64-bit versions of Windows.
The compact command acts like a storage organizer in Windows (11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP). It allows you to check if your files and folders on NTFS drives (a specific file system type) are compressed, saving precious storage space. You can also use it to compress specific files and folders, giving you more control over managing your disk space. However, using compact for compression purposes is generally recommended for advanced users as it requires understanding compression concepts and potential security implications.
The convert command lets you change your disk format from FAT/FAT32 (older formats) to the newer and more efficient NTFS format. It can improve performance and offer additional features, but be aware that it permanently changes the format and requires a backup beforehand.
Last on the list of command prompts, we have ctty. The ctty command, once used to manage input and output devices in MS-DOS and early Windows (98, 95), is no longer relevant in modern Windows systems (XP and later). This is because the underlying technology and how users interact with the system has changed significantly.
Here is the list of command prompts:
In older versions of Windows (MS-DOS and 32-bit versions), the debug command was like a mechanic’s toolbox for programmers. It allowed them to examine and modify programs line by line, but it’s not available in more recent 64-bit versions.
The dispdiag command, available in Windows versions from 11 down to Vista, serves as a diagnostic tool for gathering detailed information about your system’s display configuration. By executing this command, a log file containing these details is generated, allowing you to troubleshoot any display-related issues or simply gain a comprehensive understanding of your display hardware and software setup.
On all versions of Windows, including MS-DOS, the date command provides a convenient way to retrieve or modify the system’s current date. This functionality can be valuable for tasks like keeping system records accurate or ensuring applications work with the correct date information.
The dblspace command, dating back to MS-DOS and used in Windows 98 and 95, created and managed compressed drives using DoubleSpace technology. However, this older method was eventually replaced by a more advanced solution called DriveSpace, accessible through the drvspace command. Even DriveSpace was eventually phased out as Windows itself began handling disk compression in newer versions starting from Windows XP.
The djoin command acts like a new member registration tool. It helps you add a computer to a domain, allowing it to connect and access shared resources within that domain. This command is available in Windows versions from 11 all the way back to Vista.
The defrag command acts like a digital organizer for your hard drive. Similar to Microsoft’s Disk Defragmenter, it helps reorganize fragmented files, making your computer run smoother and access information faster. This command is available in all versions of Windows, dating back to MS-DOS, ensuring compatibility across various systems.
Old Windows (98, 95) had drvspace to manage compressed drives. This was replaced by newer ways to save space in later versions.
The deltree command, previously employed in Windows 98 and 95 to recursively delete directories and their contents, has been superseded by the enhanced capabilities of the rmdir command in modern Windows versions (XP and beyond). The introduction of the /s flag with the rmdir command rendered deltree functionally redundant, leading to its removal in later operating system iterations.
The del command, a staple since MS-DOS and still available in all Windows versions, lets you permanently remove files from your system. It’s like having a virtual eraser for unwanted data, offering the same functionality as the erase command. Remember, deleted files are gone for good, so use this command with caution and only when sure about what you’re deleting.
The dism command in Windows acts as a powerful control panel for managing features within system images. These images are like blueprints used to install or modify Windows. With dism, you can add or remove features or repair any corrupted images or system files.
In Windows and MS-DOS, the dir command is like a digital flashlight. It shows you the list of files and folders within your current location. Plus, it gives extra details like Disk ID, how many files, and their size, and the remaining space from its storage.
Available for all Windows versions and MS-DOS, the Doskey command prompt acts like a multi-tool with numerous functionalities like fixing typos or modifying commands on the fly before hitting enter, saving you time and frustration, creating shortcuts or frequently used commands, streamlining repetitive tasks with custom macros, and command recall.
In Windows XP, Vista, and 7, the diantz command, also known as makecab, served as a tool to compress files without losing any data. This is similar to how applications like WinZip or 7-Zip work today. So, if you needed to save storage space or share files efficiently in those older Windows versions, diantz or makecab were your go-to options.
The diskcopy command, a legacy tool from MS-DOS and present in older Windows versions (up to Windows 8), was used to create exact copies of floppy disks. This functionality is no longer relevant in modern computing environments, as floppy disks themselves have become obsolete. It’s important to note that diskcopy is not available in Windows 11 and 10 due to the phasing out of floppy disk drives and storage media.
The Diskcomp command is accessible to all versions of Windows, including MS-DOS, but is not supported on Windows 11 and Windows 10. Its simple task is to compare all contents of any two floppy disks.
The diskpart command prompt ultimately works for managing hard drive partitions in Windows (XP and later versions). Think of a partition as a section of your hard drive, like dividing a room with walls. With diskpart, you can create new partitions, manage all existing partitions like the format, resize them, or delete them. There is also an advanced control functionality where you can perform more even more complex tasks.
The Diskraid command is a command-line tool specific to Microsoft Windows Server environments. It allows administrators to configure and manage RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) storage subsystems.
The dosx command, exclusive to 32-bit versions of Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, and XP, served a specific purpose in the past. It activated a special mode called DPMI (DOS Protected Mode Interface). This mode allowed older MS-DOS programs to access more memory than they normally could, enabling them to run on Windows systems. However, with the increasing adoption of 64-bit architecture and the decline of MS-DOS programs, dosx and DPMI are no longer relevant for most users. They are not available in modern 64-bit Windows versions.
This command is primarily used by system administrators or network professionals who need to monitor and manage disk performance remotely on multiple computers within a network. It’s important to understand performance monitoring concepts before using diskperf to avoid making unintended changes that could impact system stability
The Dosshell command, available in MS-DOS and older versions of Windows (up to Windows 9x), served as a rudimentary graphical user interface (GUI) for managing files and directories. It offers visual file management, basic operations like copying, moving, deleting, or renaming files, and some customization offers.
The driverquery command prompt acts like a digital catalog, providing a list of all the drivers loaded on your system. It gives the specific names of driver files and offers a more user-friendly description of the driver’s purpose, like its display name, the driver type like display driver, network driver, or another type. This command prompt also provides information about whether the driver is currently loaded and functioning.
Here is the complete list of command prompts:
The echo command prompt acts as a versatile communication tool for scripts and the command line. It empowers you to display messages, control script behavior, and aid in debugging, making it a valuable asset for anyone working with these environments.
The edlin command was a basic text editor accessible from the command line in older operating systems. However, its availability is quite limited to Windows (32-bit versions and is entirely absent in modern 64-bit versions) and MS-DOS (up to version 5.0. and later versions.) Given its limited availability and the existence of more powerful and user-friendly text editors, edlin is not a practical tool for most users today. If you encounter references to it, it’s essential to be aware of its restricted accessibility in contemporary systems.
If you remember the MS-DOS editor, you’ll know about the edit command prompt, which is available only to 32-bit Windows. The edit command is used to create and edit text files directly from the command line in MS-DOS and older versions of Windows. However, its use is quite limited nowadays:
Even though not supported for modern Windows anymore, it was a tool for earlier versions that allowed users to define custom triggers based on specific log events. This command prompt could then execute actions such as launching scripts or sending notifications.
The endlocal command acts like a closing act in Windows batch files (XP and later). It ensures that any changes made to environment variables within the script don’t affect the system environment outside of the script.
The emm386 command is crucial in expanding memory accessibility for MS-DOS applications. Prior to Windows 95, MS-DOS programs were inherently limited to utilizing only the first 640 KB of system memory, regardless of the available RAM capacity. The emm386 command functioned as a workaround, enabling access to expanded memory and effectively extending the memory addressable by MS-DOS applications beyond the initial 640 KB boundary. This capability potentially improved the performance of specific MS-DOS programs by providing them with additional memory resources.
Both the erase and del commands, available in all Windows versions and even dating back to MS-DOS, offer the same functionality: permanently removing files from your system. Think of them as virtual erasers, allowing you to eliminate unwanted data with a single command. Remember, deleted files are gone for good, so use these commands with caution and only when sure about what you’re deleting.
The exe2bin command, primarily found in 32-bit versions of Windows (XP to 10), served a specific purpose in the past. It acted as a converter, transforming files in the EXE format (executable files) into a simpler binary format. It embeds compiled code within software like BIOS or device drivers. This command prompt creates files suitable for use in older operating systems with limited file format support.
The eventcreate command acts like a digital record keeper. It allows you to add custom entries to specific event logs, which are essentially digital journals that track system activities. Think of it as creating a log note within a specific category (like “Application” or “System”) to document something noteworthy that happened. This command is available in various Windows versions, from the latest Windows 11 all the way back to Windows XP.
The expand command acts like a digital unzipper for Windows and MS-DOS users (excluding 64-bit Windows XP). It helps you extract files and folders stored in a specific compressed format called Microsoft Cabinet (CAB) files.
The esentutl command, available in Windows versions from XP to 11, serves as a behind-the-scenes tool for managing databases that utilize the Extensible Storage Engine (ESE). ESE acts as a storage engine for various database applications, like Active Directory in Windows.
The exit command acts as a universal sign-off in both Windows and MS-DOS environments. It allows you to gracefully exit the command prompt (cmd.exe in Windows, command.com in MS-DOS) session you’re currently using. Think of it as closing the door on the current command prompt window, returning you to the previous interface.
Need to unpack those compressed files stored in Microsoft Cabinet (CAB) format? The extrac32 command comes to the rescue in all Windows versions. It acts like a digital unboxing tool specifically designed to extract the contents of these CAB files.
the extract command served as a helpful tool for unzipping files. Specifically, it allowed users to extract the contents of compressed archives known as Microsoft Cabinet (CAB) files. These files were commonly used in Windows 98 and 95 to store and distribute software or updates space-savingly.
Here are the F command prompts:
The fasthelp command, exclusive to MS-DOS, provides detailed information on other MS-DOS commands. It was phased out in Windows 95 and replaced by the help command.
Found in MS-DOS and 32-bit Windows systems (Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP), the fastopen command optimizes program launch times by storing a program’s hard drive location in a memory list. However, it is unavailable in 64-bit Windows versions and primarily supports older MS-DOS files.
Present in both MS-DOS and all Windows versions, the FC command facilitates file comparison, highlighting differences between individual or sets of files.
Primarily used in Windows 98, 95, and MS-DOS, the fdisk command is employed for creating, managing, and deleting hard drive partitions. It was succeeded by the diskpart command in Windows XP and onwards. Additionally, partition management is accessible through Disk Management in:
The find command searches for a specified text string in one or more files. This command is universally available across all Windows versions and in MS-DOS.
Deployed for locating text string patterns in one or more files, the findstr command is accessible in:
The finger command retrieves information about one or more users on a remote computer running the Finger service. This command is supported in:
Primarily employed for managing Filter drivers, the fltmc command enables loading, unloading, and listing these drivers. It is available in:
The fondue command, an acronym for Features on Demand User Experience Tool, is utilized to install optional Windows features from the command line. It is accessible in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 8. Additionally, optional Windows features can be installed through the Programs and Features applet in the Control Panel.
The for command executes a specified command for each file in a set of files, commonly used within batch or script files. This command is universally available across all Windows versions and in MS-DOS.
Exclusive to 32-bit versions of Windows XP, the forcedos command initiates a specified program in the MS-DOS subsystem. It is employed explicitly for MS-DOS programs not recognized.
Utilized for drive formatting in the specified file system, the format command is available across all Windows versions and in MS-DOS. Drive formatting options are also accessible through Disk Management in
The fsutil command is a versatile tool designed for tasks related to FAT and NTFS file systems. Its functionalities include the management of reparse points and sparse files, dismounting volumes, and extending volume capacities. This command is supported across multiple Windows versions, including:
The FTP command serves as a fundamental mechanism for transferring files between computers. It operates seamlessly when the remote computer functions as an FTP server. This command is uniformly accessible across all iterations of Windows.
Utilized to designate a default program for opening specific file types, the ftype command is available in various Windows editions, including:
Here are the following command prompts and their usages:
Need to identify the unique network addresses assigned to your computer’s network adapters? The getmac command prompt, available in Windows versions from XP to 11, acts like a digital name tag reader. It displays the Media Access Control (MAC) address of your system’s network controllers (also known as network adapters).
This command is available in various Windows versions, from the latest Windows 11 back to Windows XP, by using gpresult. Gpresult identifies the specific Group Policy settings that are currently in effect on your computer. It also determines where these policies originate from, such as domain controllers in a network environment or local policies defined on your machine. With it, you can use troubleshooting diagnostics and troubleshoot issues related to Group Policy configurations.
The graftabl command, present in 32-bit versions of Windows up to Windows XP and MS-DOS up to version 5.0, served a specific purpose in the past. It functioned like a special adapter for your computer’s display, allowing it to show a wider range of characters in graphical interfaces.
The goto command acts like a digital signpost within batch or script files (present in all Windows versions and MS-DOS). It allows you to control the flow of execution by directing the script to jump to a specific labeled line.
In the realm of Windows group management, the gpupdate command acts like a digital refresh button. It allows you to force an update of the Group Policy settings applied to your computer. Think of it as prompting your system to check for any recent changes or modifications made to Group Policy settings and apply them immediately, ensuring you’re working with the latest configuration.
In older MS-DOS and 32-bit Windows systems, the graphics command allowed loading a program for printing graphics. However, this functionality is no longer available in modern 64-bit Windows.
They are:
The help command is an invaluable resource. Available in all Windows versions and even in MS-DOS itself, help acts as a comprehensive guide, offering detailed explanations and usage instructions for any other command you might encounter.
Hwrcomp was a command-line tool used solely in Windows XP and earlier versions. Its purpose was to compress data collected from pen input devices like styluses for handwriting recognition. Primarily used by developers and administrators for specific handwriting recognition tasks, it’s now obsolete due to advancements in handwriting technology and how modern Windows systems handle such input.
The hostname command in Windows and MS-DOS shows your computer’s network name, which means you have to run the hostname command prompt to see it. It further changes your computer’s network name (Windows Admin only.) Use hostname new_name (replace with your desired name) to change it, but be cautious as it affects how other devices see your computer on the network.
Hwrreg, for older Windows versions, is a command-line tool solely for managing handwriting recognition settings. It allowed viewing, editing, and importing/exporting these settings but was primarily used by developers and administrators. Modern Windows systems handle handwriting input differently, making Hwrreg obsolete.
Here’s the list of Command prompts starting with I:
The iscsicli command initiates the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, facilitating the management of iSCSI. This command is available in:
The if command is used for executing conditional operations within a batch file. This command is universally available in all versions of:
Utilized to display comprehensive IP information for each network adapter using TCP/IP, the ipconfig command also supports releasing and renewing IP addresses on systems configured to obtain them from a DHCP server. This command is universally available in all Windows versions.
Designed for Windows XP, the ipxroute command exhibits and modifies information regarding IPX routing tables. Microsoft discontinued the built-in NetWare client from Windows Vista onwards, removing the associated ipxroute command.
The irftp command is utilized for transmitting files over an infrared link. It’s available in:
Exclusive to MS-DOS, the interlnk command facilitates the connection of two computers through serial or parallel links to share files and printers. Networking functions in all Windows versions have since taken over the direct computer-to-computer connection capabilities handled by the interlnk command.
Specifically designed for MS-DOS, the intersvr command initiates the Interlnk server and facilitates the transfer of Interlnk files between two computers. The networking functions in all Windows versions now manage similar direct computer connections.
Here’s the list of command prompts:
This command shows Kerberos service tickets and helps clear them out. It is available in:
Deployed for configuring connections to a Kerberos server, the ksetup command is accessible in:
Initiating the Kernel Transaction Manager utility, the ktmutil command is available in:
The kb16 command supports MS-DOS files requiring a keyboard configuration for a specific language. This command is accessible in:
It isn’t available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Originating in Windows XP, the kb16 command replaces the keyb command. It caters to the needs of older MS-DOS files.
Utilized for configuring a keyboard according to a specified language, the Keyb command finds its application in:
In subsequent versions of Windows after Windows XP, the management of keyboard language settings is now in the Region and Language or Regional and Language Options.
Here are the following:
Label your drives in Command Prompt! Use the label command to give your disks (C:, D:, etc.) friendlier names. Type label [drive letter]: [new name] (e.g., label D: Games). Need to see the current name? Just type label (without arguments). Remember, you usually need admin privileges for this.
loadfix was a memory fix-it tool for older (32-bit) Windows systems (XP to 10). Back then, some programs had memory limitations, and loadfix helped them run smoothly by making space in their preferred memory area. However, with modern systems and software, loadfix is no longer needed and isn’t even available in 64-bit Windows.
In older times (MS-DOS and Windows XP), LoadHigh (or LH) helped free up crucial memory by loading programs into a less critical area. This boosted performance, but required technical knowledge and is no longer needed in modern systems due to improved memory management.
The lpr command is commonly used in Unix-like systems to send print jobs to a computer running the Line Printer Daemon (LPD) service. While not part of Windows by default, some third-party printing tools or specific server configurations might utilize lpr in conjunction with LPD for printing purposes.
Made for Windows 11, 10, and 8, the licensingdiag acts like a diagnostic tool. It generates a text-based log and other data files containing information about your product activation status and other vital licensing details. This can help troubleshoot activation issues or simply verify your Windows license information.
The logoff command prompt operates in Windows XP to 11 to make signing out or terminating sessions easier. It aids in ending your current session and returning to the login screen.
The lh command, short for loadhigh, was a handy shortcut used in MS-DOS and Windows 95/98. It acted as a quick way to execute the loadhigh command, which helped manage memory by loading programs into a specific area to free up crucial resources. While not relevant in modern systems, encountering lh might occur in discussions about memory management in older operating systems.
The lock command, present solely in Windows 98 and 95, served a specific purpose back then. It allowed programs to directly access drives, but this functionality and command are no longer available in any version of Windows since XP.
Keeping track of performance counters in Windows? The lodctr command, available in all versions, helps update registry values related to these counters, ensuring your system has the latest information for monitoring performance.
For managing your system’s event logs and performance data, Windows (XP to 11) offers the logman command. It lets you create, manage, and view both Event Trace Sessions and Performance logs, offering functionalities similar to the Performance Monitor tool.
While the lpq command helps view print queue status on LPD-enabled systems, it’s not built-in by default in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, or Vista. However, you can enable the LPD Print Service and LPR Port Monitor features in Control Panel to use it. Remember, this command is more commonly found in Unix-like systems for managing printing.
Here are the command prompts starting with M:
The makecab command serves the purpose of losslessly compressing individual or multiple files. Often referred to as Cabinet Maker, it is accessible in:
Notably, it is analogous to the Diantz command, which was phased out post-Windows 7.
Mklink is the command to establish symbolic links, available in:
The manage-bde command configures BitLocker Drive Encryption via the command line. It is supported in;
For Windows Vista, a script named manage-Bde. wsf is available, which facilitates BitLocker tasks from the command line in that operating system when used with the script command.
Msbackup launched Microsoft Backup, a tool dedicated to backing up and restoring files exclusive to MS-DOS. Post-Windows 95, it was succeeded by Microsoft Backup and later Backup and Restore in subsequent Windows versions.
The muiunattend command initiates the unattended setup process for the Multilanguage User Interface. It is available in:
The mem command provides insights into the utilized and available memory areas and details about programs currently loaded into memory within the MS-DOS subsystem. It is compatible with MS-DOS and all 32-bit Windows versions, excluding 64-bit iterations.
Functioning to exhibit information from a text file or paginate the results of other Command Prompt or MS-DOS commands, more command is found in all Windows versions and MS-DOS.
Mountvol is the command for displaying, creating, or removing volume mount points, supported by:
The md command, a shorthand version of mkdir, is employed to create a new folder. This command is universally available across all Windows versions and in MS-DOS.
Memmaker initiates MemMaker, a tool designed for memory optimization. While it is applicable in Windows 98, 95, and MS-DOS, automatic memory optimization begins with Windows XP.
The mkdir command is dedicated to creating a new folder, functioning seamlessly across all Windows versions and MS-DOS.
Utilized to initiate Windows Installer, the msiexec command facilitates the installation and configuration of software. It is supported across:
This command configures all Windows versions and MS-DOS system devices, primarily COM and LPT ports.
The mofcomp command accurately displays the data within a Managed Object Format (MOF) file, universally available across all Windows versions.
The mount command is employed for mounting Network File System (NFS) network shares and is accessible in:
It requires operationalizing the Services for NFS Windows feature in the Control Panel.
The move command facilitates the relocation or renaming of files and directories, available in all Windows versions and MS-DOS.
Mrinfo offers insights into a router’s interfaces and neighbors, compatible with:
Initiating Microsoft Antivirus, the msav command is exclusive to MS-DOS. Microsoft Security Essentials is recommended for later operating systems, while third-party antivirus tools are available for all Windows versions.
The msg command serves the purpose of dispatching messages to users and is compatible with:
These command prompts include:
The nbtstat command prompt, available in all Windows versions, acts like a digital detective. It displays information about the remote computer’s TCP/IP connection and even provides statistics, helping you troubleshoot network issues.
The netcfg command itself is your network toolbox. It lets you view information about your network adapters and settings, change configurations (like enabling/disabling adapters), and even uninstall network components. Use it with different options (e.g., netcfg /s n for a list of installed components), but remember, modifying network settings can affect your connection, so proceed with caution.
In older Windows (XP-10) and MS-DOS, nlsfunc loaded regional settings for specific languages. This command is no longer relevant for modern systems as they handle such settings differently. While it might appear in discussions about legacy software, it’s not needed for contemporary Windows versions.
The netstat command, available in all Windows versions, acts like a digital spotlight. It lets you view active network connections on your computer, revealing which applications are communicating and which ports they’re using. This can be helpful for troubleshooting network issues, monitoring suspicious activity, or simply understanding how your system interacts with the network.
Need to translate between website names and IP addresses? The nslookup command, available in Windows XP to 11, acts like a phonebook for the internet. Enter an IP address, and it reveals the corresponding hostname. It can also do the reverse, finding the IP address for a given website name.
The net command is your network control center in Windows (all versions). Use it to view, configure, and troubleshoot various network settings. Need to see connected devices or to check adapter configurations? The net command is what you need, offering a versatile suite of functionalities for managing your network connectivity.
While net1 seems like a duplicate of net, there’s a subtle difference between the two. It was introduced as a temporary fix in older Windows (NT, 2000) for a Y2K bug in net. Though fixed, net1 remains for compatibility with older programs or scripts that specifically rely on it. So, remember: net is the go-to command for network tasks, while net1 is a relic from the past, only relevant for specific compatibility needs.
The netsh command, available in Windows XP to 11, acts like a command center. It launches the Network Shell, a powerful tool for configuring network settings on your local machine or even remotely on another computer.
In Windows Vista and 7, the nfsadmin command offered command-line management for Network File System (NFS). However, it wasn’t readily available and required enabling the “Services for NFS” feature. With the discontinuation of Service for UNIX (SFU) in later Windows versions (8, 10, and 11), nfsadmin is no longer relevant and not included in these systems.
In Windows domains (7 to 11), the nltest command acts as a network detective. It verifies secure connections between domain computers and even checks trust relationships established with other domains, ensuring smooth communication within your network.
In Windows XP, the ntbackup command was your backup companion, letting you create backups from the Command Prompt or scripts. However, it’s been retired since Windows Vista, replaced by the wbadmin command for managing backups in newer systems.
The ntsd command, exclusive to Windows XP, offered command-line debugging functionalities. However, its purpose became obsolete with the introduction of dump file support in Task Manager from Windows Vista onwards. So, while you might encounter references to ntsd in older discussions, it’s no longer relevant for modern Windows debugging tasks.
There are just two and they are:
While ocsetup lets you install extra features in Windows 7, Vista, and 8, it’s gradually being phased out. Since Windows 8, Microsoft recommends using the dism command instead for a more robust and future-proof approach to managing features.
The openfiles command prompt available in all Windows versions (XP to 11), acts like a file inspector. It displays a list of open files and folders, allowing you to disconnect them if necessary. This can help troubleshoot software conflicts or free up locked files.
Here is the list of command prompts:
The path command, available in all Windows versions and even MS-DOS, lets you set or display the search paths for executable files. This essentially tells your system where to look for programs when you try to run them.
The pause command, available in all Windows versions and even MS-DOS, halts the execution of a batch file until you press a key. This lets you review output, make choices, or simply take a break before the script continues.
In Windows Vista to 11, the pkgmgr command launches the Package Manager. This built-in tool lets you manage Windows features and packages, allowing you to install, uninstall, configure, and update them directly from the Command Prompt.
Even though the pathping command is much like tracert, the former is a more enhanced version of it. Pathping not only reveals the path but also reports on network latency (speed) and packet loss at each hop along the way, providing a more comprehensive picture of network performance.
The ping command, available in all Windows versions, acts like a digital messenger. It sends a test message (ping) to the specified computer, and a successful response confirms basic network connectivity.
The pnpunattend command (Windows Vista to 11) helps you bypass manual installation. It allows you to specify driver locations and automate the process, saving time and ensuring smooth hardware setup.
In older systems (MS-DOS, Windows 95/98), the power command aimed to conserve power by monitoring software and hardware. However, this functionality became obsolete with Windows XP, as modern operating systems handle power management more efficiently without needing a separate command.
From MS-DOS to modern Windows, the print command remains relevant. It allows you to send a text file to your printer, specifying the file and the desired output device. This straightforward command ensures your documents reach paper, making it a timeless tool for printing needs.
The powercfg command is available in Windows XP to 11. This versatile tool empowers you to manage various aspects of power settings beyond the basic options offered through the Settings menu. Leverage powercfg to optimize efficiency, analyze power usage, and configure advanced power plans, ensuring your system operates at its most efficient level.
The pwlauncher command in Windows 8 to 11 lets you control how your computer starts up from a USB drive containing Windows To Go. Use it to enable automatic booting from the USB drive, disable this option, or simply check the current settings.
The pushd command, available in all Windows versions (XP to 11), acts like a bookmark for your command prompt. It lets you save the current directory, allowing you to switch back to it later within your batch or script program. This simplifies navigation and keeps your workflow organized.
Here are the following command prompts:
While historically used to launch the QBasic programming environment in MS-DOS and Windows 95/98, the qbasic command is no longer relevant in modern systems. It wasn’t even pre-installed by default, requiring users to find it on the installation media. With the evolution of programming languages and environments, qbasic has become obsolete.
The qappsrv command, available in Windows XP to 10, locates available Remote Desktop Session Hosts on your network. It displays a list of these servers, making it easier to choose and connect to the desired remote machine for administrative or access purposes. However, this command is replaced with the query termserver command in Windows 11.
Ever wonder who’s currently using your Windows system (Vista to 11)? Enter quser, and this handy command displays information about all currently logged-on users. This can be helpful for managing user sessions or simply gaining an overview of who’s accessing the system.
The query command, available in Windows Vista to 11, acts like a service inspector. It lets you view the current status (running, stopped, etc.) of any specific service running on your computer. This can be crucial for troubleshooting service-related issues or simply checking if a service is functioning as expected.
While the name “qprocess” might suggest it displays information about running processes, it’s actually not a built-in Windows command. It’s likely referring to Qt, a popular cross-platform application framework, where QProcess is a class used for managing external processes within Qt applications. So, you won’t find a native qprocess command in Windows for viewing running processes.
For a peek into active remote desktop sessions on your Windows system (XP to 11), use qwinsta. This command displays information about all ongoing remote access sessions, helping you monitor who’s connected remotely and manage these connections if necessary.
They are:
In Windows (XP to 11), the rasautou command caters to managing Remote Access Dial-up connections. It lets you configure AutoDial addresses, which are essentially automated connection settings for remote access. This can be helpful for setting up automatic connections to remote networks or servers, but it’s important to note that dial-up connections are less common nowadays with the prevalence of broadband internet.
Next on the list of command prompts, we have rcp. The rcp command, once available in Windows XP, Vista, and 7, facilitated file copying between a Windows machine and a system running the rshd daemon (remote shell daemon). However, its use required enabling the “Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications” feature and installing additional tools.
While regini was available in Windows XP as a tool for changing registry values and permissions from the command line, it’s not recommended. The Windows Registry is a critical system component, and modifying it incorrectly can lead to unexpected behavior or even system instability.
The reset command reboots your current user session, refreshing software and hardware without a full system restart. It’s a handy tool for troubleshooting without affecting other users or background processes.
With the rasdial command on Windows (XP to 11), you can initiate connections using the network name and credentials or end them with the “/disconnect” option. While less common today, it remains useful for legacy systems or areas with limited internet options.
In Windows 8 only, recimg let you create personalized refresh images for restoring your system while keeping your files and settings. This feature is no longer needed in modern Windows versions due to the evolution of the Reset function.
Not available in Windows 7 but introduced in Windows Server 2008 and later versions, the rdpsign command lets you digitally sign Remote Desktop Protocol (.rdp) files, bolstering security by verifying their authenticity and preventing unauthorized modifications.
While rsh once let you run commands on remote machines (Windows XP, Vista, 7), its use required enabling specific features and is no longer available in Windows 8 and later. Consider alternative methods for remote execution in modern systems.
In a nutshell, rd is just a shorter way to say rmdir. Both commands, available in all Windows versions and MS-DOS, serve the same purpose: removing empty directories. So, whenever you want to delete a folder, you can use either rd folder_name or rmdir folder_name.
Reagentc is the command line to use to manage your Windows Recovery Environment (RE) in Windows 7 to 11. Use it to configure the RE boot image, enable/disable RE, and verify its status, ensuring your system has a recovery lifeline in case of trouble.
The reg command, available in Windows XP to 11, grants you command-line control over the Windows Registry, a central hub for system configurations. It lets you add/delete keys, import/export data, and view/modify registry values. Remember, caution is key as improper edits can affect system stability. Use it judiciously or seek professional guidance for advanced tasks.
While previously used in MS-DOS and early Windows versions (up to 95) to recover data from damaged disks, the recover command is no longer available in modern Windows systems (XP and later). For data recovery needs in modern Windows, consider using alternative tools or professional data recovery services.
The relog command, a retired Windows utility (pre-Windows Server 2012), helped manage server performance by extracting specific data from large performance logs. The relog command prompt converts log formats (BLG to CSV, etc.) for easier analysis. It further resamples data over different durations for alternative performance insights. While no longer included in modern systems, it served as a valuable tool for server administrators in its time.
The rename command, also known as ren, is available for Windows versions 11,10, 8, and 7 and Windows Vista and XP. This command is used to rename files and folders in various operating systems, including all versions of MS-DOS.
In Windows XP, rexec lets you run commands on remote machines with the rexec daemon. Windows Vista doesn’t have it by default, but you can enable the “Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications” and install additional tools to gain functionality similar to rsh. Forget about both in Windows 7 and later, as they’re no longer supported.
Here is the list of command prompts:
In older systems like MS-DOS, Windows 95, and 98, the scandisk command was your go-to tool for checking and repairing disk errors. However, it was eventually replaced by the more advanced chkdsk command starting from Windows XP, offering a more robust solution for maintaining disk health in modern Windows systems.
Need to control services in Windows (XP to 11)? The sc command is your command-line service center. It lets you interact with the Service Control Manager, performing various tasks like Starting, stopping, or restarting services, creating, deleting, or modifying service configurations, and querying service status and information.
In the days of Windows 95 and 98, the scanreg command served as a safety net for your system’s central configuration, the Windows Registry. It acted as a basic repair tool and backup utility, helping to maintain registry health. However, with the evolution of the Registry and the introduction of Windows XP, the need for scanreg diminished. Modern Windows systems employ more robust mechanisms to ensure registry integrity, rendering scanreg a relic of the past.
Manage custom database files (.sdb) in Windows (XP-11) with sdbinst. It lets you install, update, and uninstall these databases on multiple machines, simplifying deployment and maintenance for administrators and developers.
Automate tasks in Windows (XP-11) with schtasks. Schedule programs/commands to run at specific times, daily, weekly, or based on events. Manage existing tasks, or run/stop them on demand. Boost your efficiency with automated workflows!
Manage Windows security (XP-11) with secedit. Apply security templates for stronger defenses, analyze your current settings, and even export them for backup. This versatile tool empowers you to secure your system and stay informed.
When working with batch files in Windows (XP-11), setlocal acts like a safety net. It creates a localized environment for changes made within the script, preventing them from affecting your broader system settings. This ensures your script’s modifications are contained and don’t alter your overall environment unintentionally.
From MS-DOS to modern Windows, set lets you control environment variables – those little values that programs rely on. You can view existing ones, create new ones, or temporarily disable them to fine-tune your system’s behavior.
In Windows (7 to 11), the setspn command acts as a key manager for security within your network. It allows authorized users to manage Service Principal Names (SPNs), which are unique identifiers for service accounts in an Active Directory (AD) environment. Essentially, it helps ensure secure communication between different components within your network.
Used in MS-DOS and 32-bit Windows for file sharing, share is no longer available in 64-bit versions. While present in Windows 10-XP for compatibility, modern Windows offers dedicated file-sharing options.
Here is the list of command prompts:
If you need to stop a running program on Windows, the taskkill command prompt comes in handy. This command-line tool works like its text-based counterpart to Task Manager’s “End task” function. With this, it lets you terminate processes directly from the command prompt. The Taskkill command prompt is available for all Windows versions from XP to 11.
If you’re wondering about what runs on your Windows PC or any remote device, the tasklist command prompt offers a wide view of all active services, applications, and PID Process Identifiers.)It’s available in all Windows versions from XP to 11.
Available in all Windows versions from XP to 11, this handy tool lets you customize the title bar of your Command Prompt window. It helps make your sessions a descriptive title or simply add a personal touch to make your command-line experience more enjoyable.
If you’re looking for a way to handle your TPM virtual smart cards on Windows computers, the tpmvscmgr command works best. This tool, available in Windows 11, 10, and 8, empowers you to create and remove these secure storage devices used for authentication purposes.
If you need regaining access or full control of your files, the takeown Command Prompt for Windows works the best. There are situations where you might be denied access to a file on your Windows (Vista to 11,) the takeown command will help you locate and take control of it. Even if you had previously given control of the files to a previous user, you’d be able to regain access again. However, ensure you understand how this command works. The takeown command requires file ownership permissions.
Next on the list of command prompts, we have the time command. This is utilized to change or show the time on your Windows PC. The time command is available to all versions of Windows, including MS-DOS.
The telnet command prompt aids in connecting or interacting with all remote computers utilizing the Telnet protocol. Even though the telnet command is accessible in all Windows versions, it is disabled by default in Windows 11-7 and Vista.)
If you are looking to set up or disable TAPI client (Telephony Application Programming Interface,) the tcmsetup works the best. This command prompt is accessible or operational in Windows (11/ 10/ 8/ 7/ Vista/ XP.)
The tscon Windows command allows users to connect to various sessions over a remote desktop services session host server. Its uses are primarily directed at managing numerous Remote Desktop sessions on a server. You could also use it to switch between existing server sessions or even to disconnect from them without having to log out local users on it.
The tftp command allows users to transfer files between computers on a network using TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol.) This tool is used for minor tasks like updating firmware on network devices. However, it does lack some security features or progress tracking.
If you’re looking to control the flow of batch scripts, the timeout command in Windows is what works the best. It allows you to pause execution for a set time. This ensures that your script follows a precise consistency or rhythm. Plus, this command prompt ignores keypresses during the wait period, keeping your scripts running smoothly.
The tracerpt command prompt works like a decoder tool for event trace logs. It works for Windows (XP to 11.) All the trace logs hold a place for system behavior and other valuable patterns.
The tlntadmn command prompt is utilized as a local or remote computer running Telnet Server. This command is operable for Windows devices 11-7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. even though it is not available by default for some Windows versions, it can still be turned on by enabling the Telnet Server Windows feature. You will find this feature from “Programs and Features” within the “Control Panel” section.
The tracert command prompt is available in all Windows versions. It helps to map or trace the web travel route. It sends messages, tracks hops (routers), and displays their IP addresses (and hostnames if available). This makes it reliable for troubleshooting connections.
If you are looking for a way to display all data that is enveloped in a text file, then the type command prompt works great. This command is operable in all Windows versions, including MS-DOS.
The best way to overlook or check how your computer is performing is by using the typeperf command prompt. This command is accessible on Windows (XP to 11.) Its key functionality is giving you live stream of the performance metrics within the Command Prompt window. It also captures the performance data of log files.
If there are too many folder and you can’t see to make note of what to look for or where to find it the tree command works wonders, and available for all Windows versions, including MS-DOS. It helps users get a whole display or visual of entire folders and everything that is within it. Think of the tree command as roots leading you to a direct source.
The tsshutdn tool used to be used for shutting down or restarting terminal servers. However, this command met its end with Windows Vista onwards. However, you can alternatively use the shutdown command for same functionality. This gives a wider variety of options compared to the latter command.
The tsdiscon command, available to Windows users, allows you to disconnect from a Remote Desktop session. This session is available on a Remote Desktop Services Host server. Its functions mainly revolve around managing multiple Remote Desktop sessions and terminate your connection to a specific Remote Desktop session without needing to log users out.
The best part about the tzutil command prompt is that is helps keep your PC with the correct time globally. This command is available for Windows 7-11. It allows users to look into, change, and control the Daylight Saving Time settings. This is to ensure that you are always within the correct time zone.
Here are the list of command prompts for you to try:
The unlodctr command eliminates Explain text and Performance counter names associated with a service or device driver from the Windows Registry. This command is accessible across various Windows versions, including:
Ever accidentally erased a disk in MS-DOS? Back in the day, the unformat command could help you recover it! Unlike today’s Windows, MS-DOS offered this tool to undo a formatting mistake potentially. However, with changes in file systems, unformat became a relic of the past, disappearing from Windows 95 onwards.
The umount command is used for detaching Network File System (NFS) network shares in:
While not initially present in those mentioned above, you can still activate them by enabling the Services for NFS Windows feature in the Control Panel’s Programs and Features. However, the following:
The above-mentioned lack of the umount command is due to the discontinuation of Service for UNIX (SFU).
The unlock command restricts a program’s direct disk access, preventing it from accessing a drive. This command is exclusive to Windows 98 and Windows 95, as drive-locking functionality ceased with the advent of Windows XP.
They include:
Most users copy files, but at times, the risk of data loss is high. This is where the verify command prompt comes in handy. It is available in both Windows versions and MS-DOS. It lets users verify all files that are written on disks to ensure that they’ve been copied easily. Alternatively, it also can switch off verification mode to make copying files faster, although the errors are more frequent.
With exactly the way it sounds, the vaultcmd is a command prompt that allows users to keep track of all the login information that they store on their devices. Think of this command as a key to a vault, available for Windows 7 to 11. With the vaultcmd command, you can enter or store new commands or passwords, keep track of the ones that are saved, and even delete or clean up old credentials that are no longer necessary.
Just in case you’re wondering about the version of Windows you’re running, you simply need to run the ver command prompt. This command is available to use on all Windows versions, including MS-DOS. Think of it as the quicker way of viewing your operating system’s identity.
In order to differentiate between your drives, find the volume label or the serial numbers of your disks, the vol command works the best for it. It is accessible in all Windows versions including MS-DOS.
Windows (XP-11) offers the vssadmin command prompt to manage Volume Shadow Copy, a hidden backup feature. Use it to see existing backups and manage programs that interact with them.
The vsafe command was an early antivirus tool for MS-DOS, a bygone operating system. These days, Windows offers built-in protection (Microsoft Security Essentials for XP and later) and there are many other antivirus programs available.
Here are the command prompts starting with U:
The Whoami command allows users to obtain network user names and group information. This command is supported in:
This command launches the command-line edition of WMI, a scripting tool in Windows. It is accessible in every version of Windows.
W32tm is a command designed to troubleshoot Windows Time-related problems. This command is present in the following:
The Wevtutil command initiates the Windows Events Command Line Utility, which administers event logs and publishers. This command is supported in:
The Waitfor command facilitates the transmission or reception of signals within a system. It is accessible in:
The where command enables file search based on a specified pattern and is supported in:
The wsmanhttpconfig command oversees Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service elements. This command is supported in:
The Wecutil command oversees subscriptions to events forwarded from WS-Management-supported computers. This command is accessible in:
The Wbadmin command initiates and conducts the background tasks, providing information about prior backups, enumerating contents within a backup, and reporting the status of ongoing backups. It is supported in:
Notably, the Wbadmin command took over the functionalities of the ntbackup command, starting with Windows Vista.
The Winrm command initiates the command line edition of Windows Remote Management, facilitating secure communication management with both local and remote computers through web services. This command is supported in:
The winrs command establishes a secure command window connection with a remote host. This command is supported in:
The Wmic command initiates the Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC), providing a scripting interface to streamline the utilization of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) for managing systems. This command is accessible in:
The w32tm command troubleshoots Windows Time-related problems and is compatible with:
The winsat command initiates the Windows System Assessment Tool, which evaluates a computer’s features, attributes, and capabilities under Windows. This command is supported in:
Here are the command prompts starting with X:
This is a Windows shortcut for Extensible Wizard, which acts like an importer. It brings information, usually from a pre-made file, into the system.
Xcopy, a file copying tool available since MS-DOS and all Windows versions, offers more features than the basic “copy” command. In Windows 95 and 98, you might have seen “xcopy32” alongside the regular “xcopy”. Don’t fret – both ran the same, which is the most recent version of Xcopy.
To get the list of command prompt, which varies according to the Windows version you’re using, type help on the command prompt and click on “Enter.” You will now see the complete list of commands available. To make it easier, the commands are listed alphabetically. Command Prompt is an application that acts like a command line interpreter. You will find it available on most or all Windows operating systems. Think of it as a shortcut to execute various commands on your device. To understand the basics of CMD, think of it as an inbuilt app that lets you perform all kinds of functions. These tasks are executed via Windows graphical interface. Command prompts are used to locate, shift, share, and copy files, along with more functions. Simply open the Command Prompt window on your device and type the command you need. You will find all the command prompts on our list above. There are a few command prompt shortcuts that you can use. They are: Simply type cmd or command prompt on the taskbar search icon. Choose any command from our list according to the task you require to execute. How do I get a list of Command Prompts?
What is a command prompt?
What are the basics of command prompt?
How do I use Command Prompt?
Are the any command prompt shortcuts?
How do you get cmd commands on Windows 11?
And that’s a wrap! You now have a view and idea of the entire list of command prompts available for your Windows devices. Also, note that for extra security, always consider using a VPN for Windows. The FastestVPN Windows app comes with high-end encryption, has fast speeds, and paves access to the best streaming services, apps, and websites.
Take Control of Your Privacy Today! Unblock websites, access streaming platforms, and bypass ISP monitoring.
Get FastestVPN
© Copyright 2024 Fastest VPN - All Rights Reserved.


Don’t miss out this deal, it comes with Password Manager FREE of cost.
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.


